Frequently we get the question, “Why do I need your remote visual assistance solution when I can just use a normal video call?”—a valid question. So let's compare the two and see which one suits your needs.
XMReality Blog

Frequently we get the question, “Why do I need your remote visual assistance solution when I can just use a normal video call?”—a valid question. So let's compare the two and see which one suits your needs.
Suppose you are relatively new to remote visual assistance solutions. In that case, seeing it as a more expensive version of FaceTime, Skype, WhatsApp, GoogleDuo, and other video call solutions is a common misunderstanding. So, let’s point out the distinguishing differences between remote video support, also called visual assistance, and a video call.
If you aren’t quite sure what we term "remote visual assistance" or as we also call it "remote video support" means, check out this page where we explain the concept in depth.
First, the entire purpose of using each solution is very different. Yes, both solutions focus on connecting people, but the main reason to join is fundamentally different.
With a regular video call, you usually want to have a conversation with your friends or family where you also can see each other - to make it more similar to meet “IRL.” So most of the time, you look at each other, even if you might turn the camera around to show your cat doing something funny.
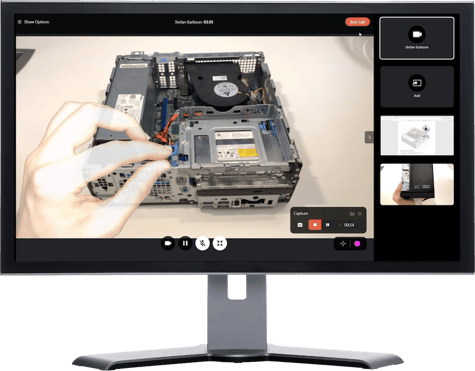
In a remote video support call, the purpose is not to look at each other but jointly at the same problem. Instead of ‘person one’ seeing ‘person two’ and vice versa, both parties are looking at the same video feed in a remote video support solution. If I connect with a service technician to get help assessing a malfunctioning printer, seeing the face-to-face video is not ideal. It’s much easier for us to collaborate if we both see a clear image of what my camera shows (the printer), versus me, only seeing a miniature version up in the left corner of the screen.
So the purpose of each solution is entirely different, resulting in more differences between the two.

Many video calls solutions, such as Google Duo and Messenger, have Augmented Reality features to add funny effects or accessories to your face. And yes, a digital pair of bunny ears might be the key to success for a normal video call, but they are less helpful when trying to help someone solve a problem or inspect a piece of equipment.
With remote video support, you can access tools to better guide the person you are talking with. So, if I show you my malfunctioning printer, which you, for the benefit of this example, are an expert on, you can use the pointer to show where I need to press to open the control panel. You can also freeze my video feed and draw on it, showing how to turn on one function or dial down another. This simple example highlights what visual assistance is designed for, connecting you with an expert who can help you through the different steps.
Online meeting platforms like Microsoft Teams and Zoom are built for meetings, video conferencing, webinars, and online events. Participants can see each other on the call and share their screens, often used to present a PowerPoint presentation.

In Teams & Zoom, you can also turn your mouse into a laser pointer to draw attention to something on a slide. But with only one presenter at a time, the person presenting will have to stop sharing their screen before anyone else can share. In a remote guidance call, jumping between views is much easier. You can see what the other person is seeing, share your screen, share a picture, draw or point on the screen, and then go back to see the live image of the problem you are trying to solve.
Imagine that you open a control panel and find yourself looking at seven cables in a row. You are now being told to pull out the second left green cable. Now add to the situation that you and the person who is guiding you speak a different language. With a visual assistance solution, you can overcome language barriers by using the pointer function to point at the specific cable and confirm that this is the right cable to pull.
A poor internet connection can easily disrupt your call by freezing the video or cutting out the sound when you call people via FaceTime or WhatsApp. That is because it requires a higher bandwidth when two video streams go simultaneously. You only need one video stream if you use a remote video support solution optimized for visual assistance. This is lighter on the network and, therefore, easier to use in remote locations.
Another option to conduct a remote video support session when the internet connection is failing is to record the session and show the recorded video on the mobile application once the connection is restored. There is no threshold to start recording, and if you often get support cases on the same machine, you can record the session once and save it for later use. You can also conduct remote support calls on a slow-motion video if you work with high-speed machines.
Typical for video call solutions is that most of the time, both parties in the conversation need to have the same app installed. This is not a big obstacle when you connect regularly - usually, you check what type of video apps each person has, and you might discover that both have Messenger and decide to go for that.
In a business setting, this is slightly more complicated. More often than not, you might not be connected with your intended counterpart on a common solution. If you work as a service technician providing support, you must most likely connect with new people daily. For every one of these interactions, you don’t want to waste time on figuring out which video call solution to use this specific time - instead, you want one that works with anyone. Which is exactly what our visual assistance solution is built for.
With XMReality, only the person who initiates the call needs the app (or desktop application) installed. You can then share a link with the person you want to call; you can send it as a text message, email, or any other chat function you might be connected through. When the other person clicks on that link, a call will be initiated through their web browser, so no need for them to download an app or create an account.
It’s just as simple as that - they need to click on a link and it doesn't matter what type of smartphone they have as long as it has an internet connection and a camera. You can, of course, also place calls between two people who have the app as well; then, you don’t need to send a link; just add the other person as a contact.
Using XMReality is just as easy as making a regular video call and even more accessible since you can connect with anyone you like, regardless of whether they have the software. It’s great when you want to solve problems around malfunctioning equipment, perhaps do a remote inspection as part of your preventative maintenance, or sometimes train new employees in the field. But if you need to catch up with a friend or a colleague and have a friendly chat, a normal video call is what I would recommend. So each solution has its own intended use, which it is optimized for.
Since XMReality is built with simplicity in mind, we can guarantee that you can implement the software quickly, with minimum training and no complicated integrations or software setups required. All of this makes for excellent scalability within your organization and a fast return on your investment.